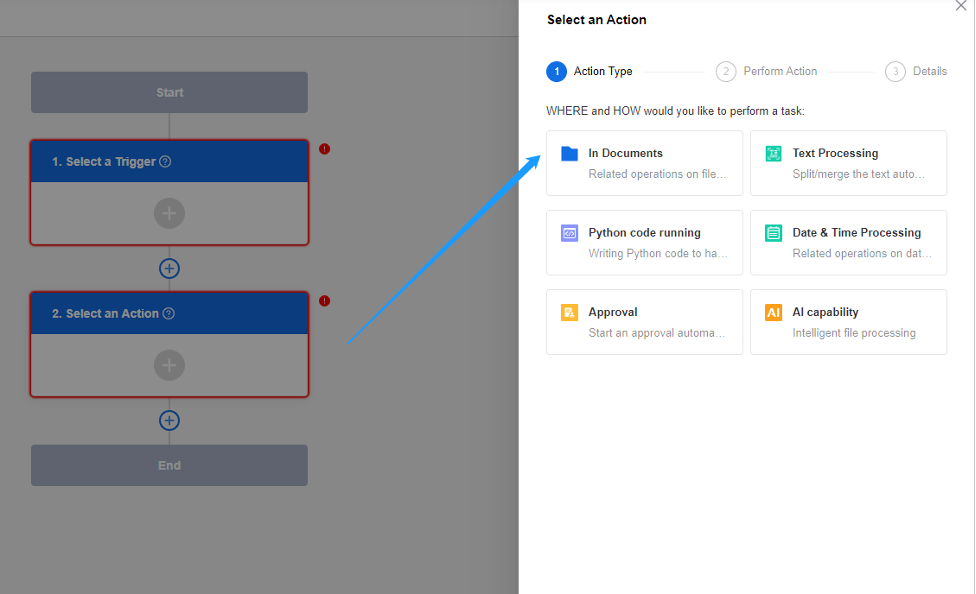
In some business scenarios, processing a large amount of data such as copying, moving or deleting files by manual wastes time and energy, which can easily go wrong. With automated flows, you can collaborate with other colleagues, extract file content, collect data, sync data, get notifications, and much more.
For example, you can automate these tasks:
- Start an approval when a file is uploaded in a target folder
- Add catalogues to this folder when creating new folders
- Save the attachment of the sheet file to a specified directory
- Archive the files based on their time of creation
- ...
Automate your business flows with 30+ actions and 10+ templates. No code required.
Core Concepts of Automated Flow
In the previous part we learned about the overview and different scenarios of automated flow. Here we'll introduce some basic concepts to you before building your own flow.
"When a pre-set trigger event happens and after the condition is met, perform the pre-set action event."
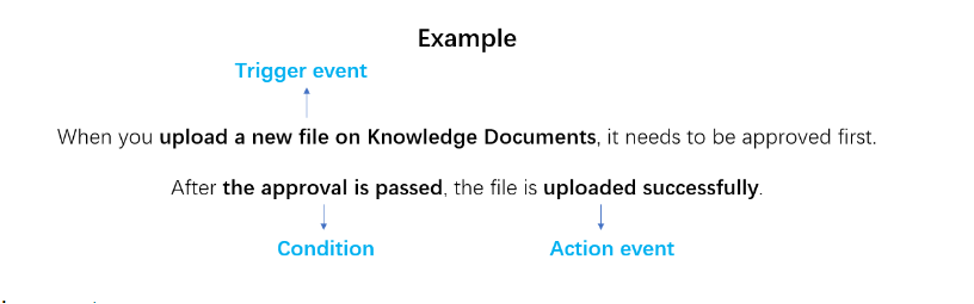
› Trigger event: The trigger event is the beginning of a flow, and the status of which is used to judge whether to start to perform a flow. In the above example, "upload a new file on Knowledge Documents" is the starting point of this flow.
The most common used trigger event types are: By event, By manual, After form completion and By schedule.
• By event: Set the specified event as the trigger, mostly applied to the scenarios where data creation or data change is involved in dealing with files and folders. In other words, you need to select a target folder, and when you create, upload, copy, move or delete a file under this folder, perform the next action. For example, when creating a folder, add the name of the folder to the catalogue template automatically.
• By manual: Trigger by manual refers to the process of manually clicking after setting up an automated task to perform the next action. Different from triggering by event, the object that is manually triggered is a file or folder that has already been uploaded to a certain folder so that you click "Run" to trigger the next action required. It is mainly used in scenarios involving data synchronization. For example: A folder which was created long time ago is stored in Documents and can be automatically archived to another specified folder.
• After form completion: Set form submission as a trigger event, suitable for scenarios where forms are used for collaborative work, such as document permission application, circulation management of approved contract files, and initiation of quota expansion application by filling out forms.
• By schedule: The trigger event would be a fixed period or time point, which can be applied to the message notification scenarios. During the office work, some tasks are required to be done in a specified time like when you need to archive the files to a target location regularly, you should select the time and interval to trigger this task and this task will run every x minute(s), x month(s), x year(s), etc.
› Action Condition: Also known as logical action, and only when this condition is met will the set action event be performed. Simply put, it refers to the branch in a flow. The running order of the branch is matched from left to right, and only when the condition of the previous branch is met can the process of next branch be executed. In the above example, "approved → upload the file" can be understood as Branch 1 in the process. If the approval is not approved, the file will be deleted, and then "approved → deleted the file" is Branch 2.
› Action event: Action event refers to the specified action run by the flow automatically after the previous trigger event occurs and the conditions are met. In the above case, after the approval is passed, "upload the file in Knowledge Documents" is the action the flow performs in the end.
Automated Flow work
You may start your automated flow just by setting the "trigger" and "action".
Step1. Set the Trigger
A trigger is an event that starts an automated flow. Say when uploading a file, add tags to this file—the trigger would be "uploading a file". The trigger is the beginning of the flow, and only one trigger can be configured during this flow, which cannot be deleted as well.
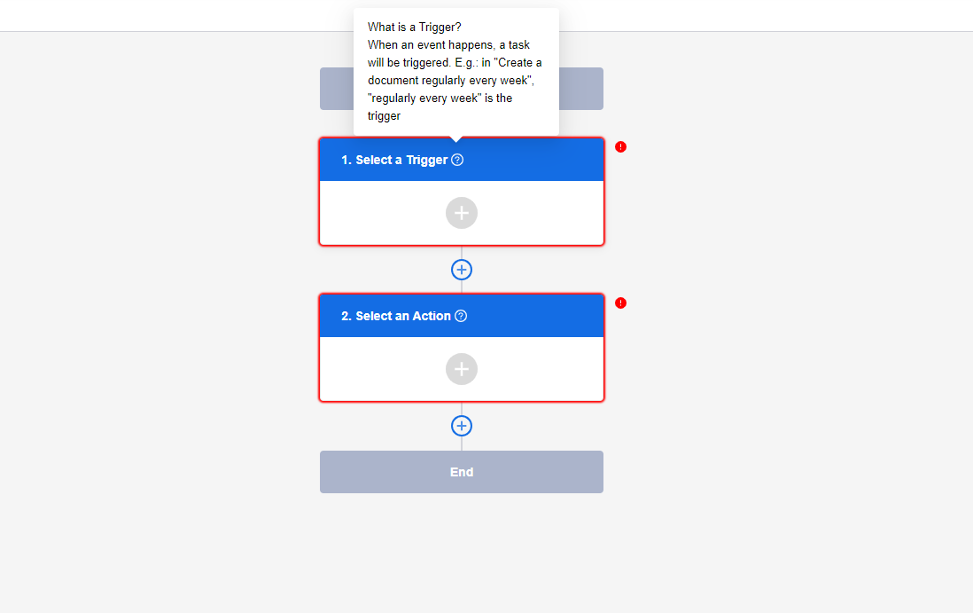
Step2. Set the Action
An action is after the trigger event happens, the specific event that is performed for processing or delivering data. Say you want to inform relevant staff when the file is being updated—the action would be "inform relevant staff". In the same flow, you may set one or more actions.